Different Types of Ethernet Cables
Did you know that the type of Ethernet cable you use can make or break your network’s performance? In today’s fast-paced digital world, where milliseconds matter, choosing the right Ethernet cable is more critical than ever. It doesn’t matter whether you’re streaming, gaming, or managing a data center. These hidden heroes keep home Wi-Fi and big networks running, even though many don’t notice them.
Understanding the types of Ethernet cables is key to delivering reliable, high-speed internet for network installers, IT managers, home networking enthusiasts, electrical contractors, and resellers.
This blog’ll break down Ethernet cables’ evolution, categories, and use cases, from the trusty Cat5e to the powerhouse Cat8. By the end, you’ll know exactly which cable suits your needs, ensuring seamless connectivity for any setup.
Keep reading to discover which Ethernet cable is perfect for your needs!
Table of Contents
The Evolution of Ethernet Cables
Ethernet cables have evolved dramatically since their debut in 1980, when the first standard delivered a modest 10 Mbps. As technology advanced, the demand for faster, more robust networking solutions also increased. This sparked the development of various cable categories, improving speed, bandwidth, and performance.
- Cat1 to Cat4: Early cables like Cat1 were designed for telephone systems, while Cat3 and Cat4 supported basic networking at 10 Mbps and 16 Mbps, respectively.
- Cat5: A game-changer for computer networks, Cat5 brought speeds up to 100 Mbps, laying the groundwork for modern connectivity.
- Cat5e and Beyond: Enhanced versions like Cat5e reduced crosstalk, while Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, and Cat8 pushed speeds into the gigabit range and beyond, catering to today’s high-bandwidth needs.
This evolution reflects the growing demands of networking, from basic internet access to data-intensive applications like 4K streaming and cloud computing.
Categories of Ethernet Cables
Ethernet cables are classified into categories (Cat), each with unique specifications for speed, bandwidth, and use cases. Below, we explore the most common types, their features, and their pros and cons.
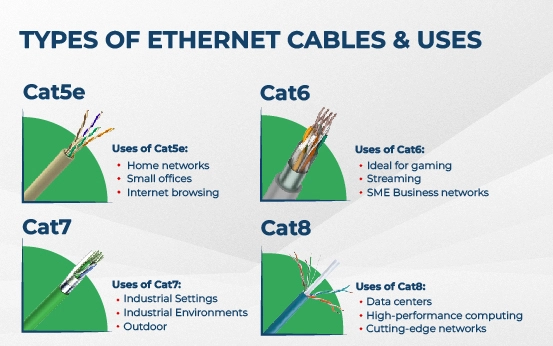
Cat5e Ethernet Cables
Description: Cat5e (Category 5 enhanced) is an upgraded version of Cat5, supporting speeds up to 1 Gbps and frequencies up to 100 MHz.
Common Uses: Perfect for home networks, small offices, and general internet browsing.
Pros:
- Affordable and widely available.
- Compatible with most devices.
Cons:
- Limited speed and bandwidth.
- Susceptible to interference over long distances.
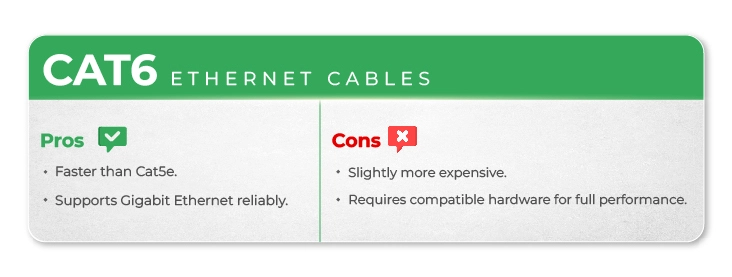
Cat6 Ethernet Cables
Description: Cat6 cables handle speeds up to 10 Gbps (over 55 meters) and frequencies up to 550 MHz, with improved shielding.
Common Uses: Ideal for gaming, streaming, and small to medium business networks.
Pros:
- Faster than Cat5e..
- Supports Gigabit Ethernet reliably.
Cons:
- Slightly more expensive.
- Requires compatible hardware for full performance.
Cat6a Ethernet Cables
Description: Cat6a (augmented) doubles the frequency to 500 MHz, maintaining 10 Gbps speeds over 100 meters.
Common Uses: Suited for data centers, enterprise networks, and high-bandwidth setups.
Pros:
- Higher bandwidth and reach 10 Gbps.
- Enhanced shielding reduces interference.
Cons:
- Thicker and less flexible, complicating installation.
- Higher cost than Cat6.
Read in detail about the types of Ethernet cables
Cat7 Ethernet Cables
Description: Cat7 supports speeds up to 10 Gbps at 600 MHz, with robust shielding for minimal interference.
Common Uses: Great for industrial settings or environments with high electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Pros:
- Superior performance in noisy environments.
- Future-ready for higher speeds.
Cons:
- Expensive and requires GG45.
- Overkill for most home setups.
Cat8 Ethernet Cables
Description: The latest standard, Cat8 delivers speeds up to 40 Gbps and frequencies up to 2000 MHz over shorter distances (30 meters).
Common Uses: Designed for data centers, high-performance computing, and cutting-edge networks.
Pros:
- Unmatched speed and bandwidth.
- Exceptional shielding for top-tier performance.
Cons:
- Very costly and unnecessary for typical applications.
- Limited distance for maximum speeds.
Understanding types of Ethernet Cable Speeds and Performance
The performance of an Ethernet cable hinges on its category, construction, and external factors. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Speed: Measured in Mbps or Gbps, this indicates data transfer rates. For example, Cat5e tops out at 1 Gbps, while Cat8 reaches 40 Gbps.
- Bandwidth: Measured in MHz, this reflects the cable’s capacity to handle data frequencies, higher MHz means more data at once.
- Interference and Length: Crosstalk, EMI, and cable length can degrade performance, especially in lower categories.
Here’s a handy Ethernet cable speed chart:
| Cable Type | Max Speed | Bandwidth | Max Distance |
| Cat5e | 1 Gbps | 100 MHz | 100m |
| Cat6 | 10 Gbps | 250 MHz | 55m |
| Cat6a | 10 Gbps | 500 MHz | 100m |
| Cat7 | 10 Gbps | 600 MHz | 100m |
| Cat8 | 40 Gbps | 2000 MHz | 30m |
Choosing the right cable balances speed needs with practical considerations like distance and cost.
Choosing the Right Ethernet Cable for Your Needs
Your ideal Ethernet cable depends on your specific application. Here’s the detailed overview of how you can choose a cable according to your need and requirement:
For Home Networking
- Recommendation: Cat5e or Cat6.
- Why: These cables offer reliable speeds (up to 1 Gbps or 10 Gbps) for browsing, streaming, and smart home devices at an affordable price.
- Tip: Opt for Cat6 if you’re planning a Gigabit internet upgrade.
For Gaming
- Recommendation: Cat6 or Cat6a—the best Ethernet cables for gaming.
- Why: Low latency and high speeds (up to 10 Gbps) reduce lag, ensuring smooth online gameplay.
- Tip: Use shorter lengths (<55m) with Cat6 for peak performance.
Read our detailed blog on why Cat 6 is suitable for gaming.

For Business and Enterprise
- Recommendation: Cat6a or Cat7.
- Why: These support high-bandwidth applications, multiple devices, and future growth, making them ideal for offices and data centers.
- Tip: Choose Cat7 for environments with heavy machinery or EMI.
For Outdoor and Industrial Use
- Recommendation: Shielded Cat7 or Cat8.
- Why: Enhanced durability and interference protection suit harsh conditions like construction sites or outdoor installations.
- Tip: Look for weatherproof jackets for added resilience.
Shielded vs. Unshielded Ethernet Cables
Ethernet cables come in two flavors: shielded twisted pair (STP) and unshielded twisted pair (UTP).
- Unshielded (UTP):
- Best for: Homes and offices with low EMI.
- Pros: Flexible, affordable, easy to install.
- Cons: Prone to interference in noisy settings.
- Shielded (STP):
- Best for: Industrial areas, near power lines, or data centers.
- Pros: Reduces crosstalk and EMI for consistent performance.
- Cons: Stiffer, pricier, and harder to work with.
For most users, UTP suffices, but STP is a must in high-interference zones.
Ethernet Cable Length and Its Impact
Cable length affects signal quality and speed. Each category has a maximum length for optimal performance:
- Cat5e: 100 meters at 1 Gbps.
- Cat6: 55 meters at 10 Gbps, 100 meters at 1 Gbps.
- Cat6a: 100 meters at 10 Gbps.
- Cat7: 100 meters at 10 Gbps.
- Cat8: 30 meters at 40 Gbps.
Beyond these limits, signal degradation occurs, slowing your network. For long runs, consider repeaters or higher-category cables.
Future-Proofing Your Network with the Right Cable
Future-proofing means picking a cable that will work for years ahead. Investing in a higher-category cable now can save you from upgrades later. While Cat5e meets basic needs, Cat6 or Cat6a offers headroom for faster internet plans and emerging tech like 8K streaming or IoT. For businesses, Cat7 or Cat8 ensures scalability.
Think long-term—your network deserves it!
For more insights on network planning, check out HowStuffWorks’ guide to Ethernet!
Conclusion
Ethernet cables are the backbone of wired networking, and choosing the right type is essential for peak performance. From Cat5e’s affordability to Cat8’s blazing speeds, each category serves a purpose, whether you’re a home user, gamer, IT manager, or contractor. Consider your speed, distance, and environment to pick the perfect cable.
As someone who’s set up countless networks, I can’t stress enough how important it is to choose the right Ethernet cable for your needs. It’s not just about speed but reliability, durability, and preparing for tomorrow’s tech.
Ready to upgrade your network?
Explore our range of high-quality Ethernet cables at Jourmik.com today!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What’s the difference between Cat6 and Cat7 cables?
Cat6 supports 10 Gbps at 250 MHz, while Cat7 offers the same speed at 600 MHz with better shielding, making it ideal for high-interference areas. - Can I use Cat8 cables for home networking?
Yes, but Cat8’s 40 Gbps speed is overkill for most homes. Cat5e or Cat6 are more cost-effective choices. - How do I know which Ethernet cable is right for my business?
Assess your network size, speed needs, and growth plans. Cat6a or Cat7 are great for scalability and performance. - What’s the maximum length for an Ethernet cable?
Most cables maintain rated speeds up to 100 meters, though Cat6 (10 Gbps) drops to 55 meters, and Cat8 to 30 meters. - Are shielded cables necessary for home use?
Rarely—unshielded cables work fine unless you’re near heavy EMI sources like power lines. - Can I mix different categories of Ethernet cables in my network?
Yes, but performance will be limited by the lowest-category cable. - Do Ethernet cables affect internet speed?
Absolutely—using an outdated cable can cap your speed below your plan’s potential.
