Shielded Vs Unshielded Cables: What You Need to Know

Did you know that electromagnetic interference (EMI) can reduce your network speeds by up to 50%? With the rise of smart homes and high-speed internet demands, choosing the right Ethernet cable isn’t just about speed, it’s about reliability.
Ethernet cables are the backbone of any network, and understanding the differences between shielded and unshielded options can help you optimize your setup. The correct cable can make all the difference from reducing interference to ensuring high-speed data transmission.
Choosing the right type of Ethernet cable can significantly affect network reliability, speed, and overall performance. This article aims to clarify the differences between shielded vs unshielded cables, helping network installers, IT professionals, and even home enthusiasts make informed decisions.
Keep reading to discover which Ethernet cable is perfect for your needs, and why thousands of IT pros trust Jourmik.com for their cabling solutions!
Table of Contents
Overview of Ethernet Cable Types
Ethernet cables, available in various categories (Cat5e, Cat6, Cat7, Cat8), form the backbone of wired networking. These cables are essential for establishing high-speed connections in both home and commercial settings.
Read More: Different types of Ethernet Cables
Categories of Ethernet Cables
Ethernet cables are generally categorized based on their performance, with Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat7 being the most common in residential and commercial use. As the category number increases, i.e, from 5, 6, 7 to 8, the performance capabilities, such as higher speeds and greater shielding to combat interference, also go up.
To better understand the technical standards that govern these categories, you can refer to the IEEE Standards for Ethernet Cables.
Shielded vs. Unshielded Ethernet Cable: Basic Differences
The key difference distinguishing each cable from the other lies in protecting against external interference. Shielded cables contain additional layers designed to block electrical noise, while unshielded cables rely solely on the insulation around the wires.
What is Shielded Ethernet Cable?
Shielded Ethernet cables have an extra layer of protection that shields the internal wires from external interference, enhancing the cable’s overall durability and reliability.
Definition and Construction of Shielded Cables
Shielded Ethernet cables are equipped with a metallic shield that surrounds the twisted pairs of wires inside the cable. This shield acts as a barrier against electromagnetic and radio frequency interference (EMI and RFI).
Types of Shielding: Foil vs. Braided
- Foil Shielding: A thin layer of foil is wrapped around the wires to protect against external interference.
- Braided Shielding: A mesh of copper strands envelopes the cables, offering greater flexibility and protection, especially in environments with high interference.
Benefits of Shielded Ethernet Cables
- Reduced Interference: Shielding protects against electromagnetic and radio frequency interference (EMI and RFI), ensuring more stable and reliable data transmission.
- Improved Signal Quality: Shielding helps maintain the integrity of signals, particularly in environments with heavy machinery or electrical equipment that can disrupt network performance.
- Enhanced Durability: The extra layer of protection can also make shielded cables more durable in harsh environments.
What is Unshielded Ethernet Cable?
Unshielded Ethernet cables, or UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cables, are the most common type of Ethernet cables used today. They consist of pairs of wires twisted together without any additional protective shielding.
Definition and Construction of Unshielded Cables
These cables have simple construction, with twisted pairs of wires that help reduce crosstalk (interference between the pairs). However, unlike shielded cables, they lack any shielding to protect against external interference.
Common Uses of Unshielded Cables
- Home Networks: Unshielded cables are sufficient for most residential setups with minimal external interference.
- Cost-effective Solutions: Unshielded cables are cheaper and more flexible, making them ideal for budget-conscious setups.
Advantages and Limitations
- Advantages: Affordable, easy to install, and perfectly suitable for environments with minimal interference.
- Limitations: Prone to external interference, making them less reliable in environments with heavy electrical equipment or high noise levels.
Key Differences Between Shielded and Unshielded Ethernet Cables
Let’s break down the main differences between shielded and unshielded Ethernet cables:
Physical Structure and Design
Shielded cables feature a layer of shielding (foil or braided) surrounding the wires, while unshielded cables rely solely on the twisted pairs for noise reduction.
Interference Protection
- Shielded: Effective at blocking interference from electrical equipment and external sources.
- Unshielded: More susceptible to electromagnetic and radio frequency interference.
Cost Comparison
Shielded cables tend to be more expensive due to the additional shielding material. Unshielded cables are cheaper and more flexible, making them ideal for simpler, low-interference environments.

Installation Complexity
Shielded cables are slightly more complex to install, requiring grounding to avoid potential electrical hazards. Unshielded cables are straightforward to install and do not require grounding.
Interference Protection: Why It Matters
External interference can disrupt network performance, leading to slow speeds and connection issues. Understanding how shielding protects against this interference is key.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
EMI occurs when electrical devices generate electromagnetic fields that interfere with your Ethernet cables’ signals. Shielded cables provide a protective barrier to block these fields.
Radio Frequency Interference (RFI)
RFI arises from the interference caused by radio signals, which can distort data transmission. Shielded cables offer enhanced protection against this kind of interference.
Pro Tip: Due to their protective features, shielded cables are prime locations for using in buildings with heavy machinery and environments with high electrical activity.
Performance and Speed: Does Shielding Impact Network Speed?
While both shielded and unshielded Ethernet cables can support high-speed internet connections, the additional protection offered by shielded cables ensures that data integrity is maintained in high-interference environments.
Network Speeds for Shielded vs. Unshielded Cables
- Unshielded Cables: Sufficient for most home networks and basic office use.
- Shielded Cables: Ideal for high-performance networks that require consistent, uninterrupted signal transmission, especially for tasks like streaming, gaming, and large file transfers.
Impact of Shielding on High-Speed Data Transmission
The extra protection in shielded cables ensures that high-speed data can flow without degradation from external noise.
Use Cases for High-Speed Networks
- Data Centers
- Video Conferencing
- POE (Power over Ethernet) Systems
Comparative Performance Chart:
| Cable Type | Maximum Speed | Max Distance (For 10Gbps) | Interference Protection | Use Case |
| Unshielded Ethernet Cable | Up to 1Gbps | 100 meters | Minimal (susceptible to EMI) | Home networks, small businesses |
| Shielded Ethernet Cable | Up to 10Gbps | 55 meters | High (resistant to EMI/RFI) | Data centers, industrial setups |
Grounding in Shielded Ethernet Cables
Grounding is essential for shielding the cable so it works effectively. The shielding might not perform its job without proper grounding, and the cable could act as an antenna, amplifying interference.
Why Grounding is Crucial
Grounding allows the shielded layer to safely discharge any electrical charges, ensuring that interference doesn’t affect the data signal.
How to Properly Ground Shielded Ethernet Cable
- Connect the shielded layer to a grounding point at both ends of the cable.
- Use a grounding module or connect directly to a grounding bus bar in network infrastructure.
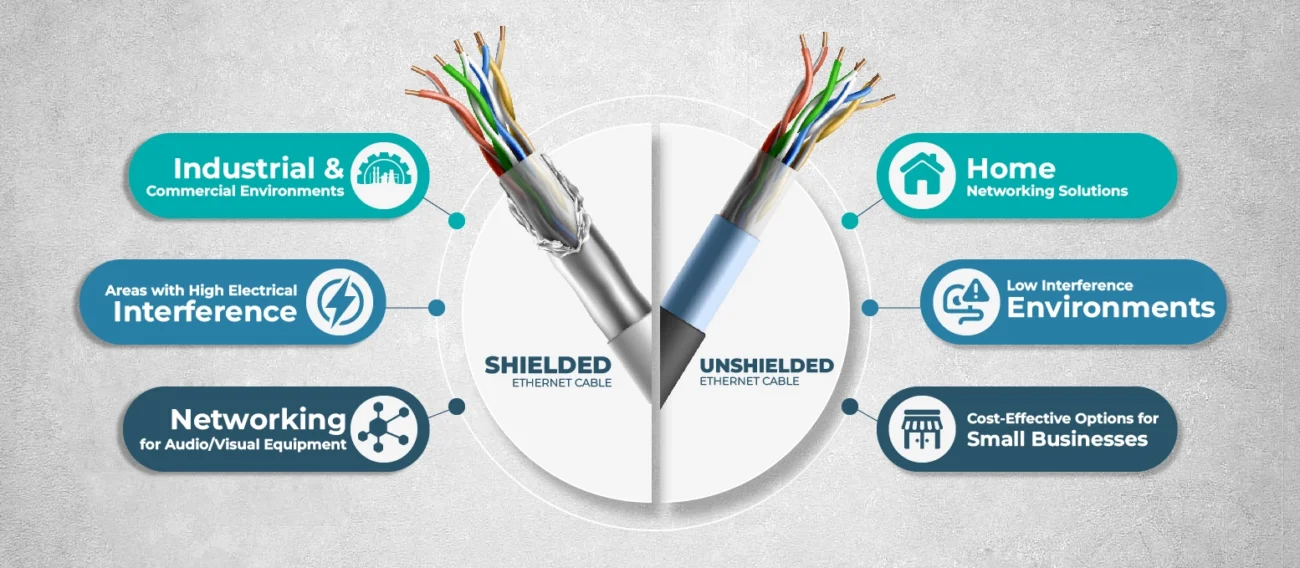
When to Use Shielded Ethernet Cable
Shielded Ethernet cables are highly beneficial in certain environments:
Industrial and Commercial Environments
Manufacturing plants, hospitals, and large office buildings often experience high levels of electromagnetic interference. Shielded cables can prevent data loss or slowdowns in these settings.
Areas with High Electrical Interference
Near power transformers, heavy machinery, or high-voltage systems, shielded cables prevent disruptions that could impact data integrity.
Networking for Audio/Visual Equipment
In installations involving sensitive audio or video equipment, shielded cables ensure clear, uninterrupted transmission of high-quality signals.
When to Use Unshielded Ethernet Cable
Unshielded cables are an excellent choice for home networks, small businesses, or environments where electrical interference is minimal.
Home Networking Solutions
Most residential settings don’t require the added protection of shielded cables, making unshielded cables an affordable and efficient solution.
Low Interference Environments
If you’re setting up a network in an area with minimal electrical equipment, unshielded cables will provide sufficient protection against interference.
Cost-Effective Options for Small Businesses
Unshielded cables offer a cost-effective, simple solution for small businesses with less demanding network requirements.
Popular Ethernet Cable Standards
Ethernet cables come in various categories designed for different performance levels. The most common ones include:
Cat5e Ethernet Cables
Cat5e cables are designed for standard home and office use, supporting speeds up to 1Gbps.
Cat6 Ethernet Cables: Shielded vs. Unshielded
Cat6 cables offer enhanced performance and can support speeds up to 10Gbps over short distances. Depending on the need for interference protection, both shielded and unshielded versions are available.
Cat7 and Cat8: Advanced Shielding and Performance
Cat7 and Cat8 cables provide even higher performance and come with advanced shielding for use in professional data centers and environments with high interference.
Pros and Cons of Shielded and Unshielded Cables
Each cable type has distinct advantages and disadvantages, influencing the decision based on cost, environment, and installation needs.
Unshielded Cables (UTP):
Pros:
- Cost-Effective: Generally cheaper, making them budget-friendly for many users.
- Ease of Installation: Lighter and more flexible, easier to route through walls and ceilings.
- Sufficient for Most Needs: Adequate in low to moderate interference environments.
Cons:
- Susceptible to Interference: Vulnerable to EMI and RFI, leading to data errors or slower speeds in high-interference areas.
- Limited in High-Speed Networks: May not perform optimally for very high speeds or long runs due to increased interference susceptibility.

Shielded Cables (STP):
Pros:
- Enhanced Protection: Superior defense against EMI and RFI, ensuring consistent performance in challenging environments.
- Reliable in High-Interference Areas: Ideal for data centers, industrial settings, and areas with significant noise.
- Future-Proofing: Can handle higher data rates effectively in interference-prone environments as networks evolve.
Cons:
- Higher Cost: More expensive due to additional materials and manufacturing, with a 20-50% price increase over UTP.
- Less Flexible: Thicker and less flexible, complicating installation in tight spaces.
- Grounding Requirements: Requires proper grounding at both ends, adding complexity to installation and maintenance.

Cost Comparison: Shielded vs. Unshielded Ethernet Cables
Price Differences Between Shielded and Unshielded Cables
Shielded cables are typically more expensive than unshielded cables due to the additional materials and manufacturing processes involved.
Long-Term Value of Shielded Cables
While shielded cables may have a higher upfront cost, their durability and protection against interference can make them a more cost-effective solution in high-demand environments.
Is the Investment in Shielded Cables Worth It?
The extra investment in shielded cables can be worthwhile for high-performance networks, especially when network reliability is critical.
Common Misconceptions About Shielded and Unshielded Cables
Debunking Myths About Performance
One common misconception is that shielded cables consistently outperform unshielded cables. However, the effectiveness of shielded cables largely depends on the presence of interference in the environment.
Understanding Cable Durability and Lifespan
While shielded cables are more durable in harsh environments, unshielded cables still provide sufficient longevity in most home or low-interference settings.
How to Choose the Right Ethernet Cable for Your Network
Choosing between shielded and unshielded Ethernet cables depends on factors like the level of external interference and the performance requirements of your network.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Shielded and Unshielded Cables
- Environmental conditions (electrical interference)
- Network performance needs
- Budget considerations
How to Assess Your Network’s Needs
- Evaluate the level of interference in your installation area.
- Determine your speed and data transfer requirements.
Expert Recommendations for Various Use Cases
- For high-interference environments: Shielded cables are the better choice.
- For home use or small offices: Unshielded cables are generally sufficient.
Conclusion
Choosing between shielded and unshielded Ethernet cables is an important decision that impacts your network setup’s performance, reliability, and cost. You can make a more informed choice by understanding the differences and evaluating your specific needs. Shielded cables offer superior protection for environments with high interference, while unshielded cables are more cost-effective for low-interference scenarios.
Ready to upgrade your network?
Explore a wide range of high-quality Ethernet cables at Jourmik.com to ensure seamless connectivity for your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What’s the Difference Between Cat6 and Cat7 Cables?
Cat6 supports speeds up to 10Gbps for shorter distances, while Cat7 offers additional shielding and supports speeds up to 40Gbps over short distances.
2. Can I Use Cat8 Cables for Home Networking?
Cat8 cables are designed for data centers and high-performance systems and are typically unnecessary for most home networking needs.
3. What’s the Maximum Length for an Ethernet Cable?
The maximum length for Ethernet cables is 100 meters (328 feet) for most Cat5e and Cat6 cables. Beyond that, signal degradation can occur.
4. Are Shielded Cables Necessary for Home Use?
Shielded cables are typically unnecessary for home networks unless your home is prone to significant electrical interference.
5. How Do I Know Which Ethernet Cable is Right for My Business?
Consider your environment, network demands, and budget. Shielded cables are ideal for high-traffic networks with interference, while unshielded cables are suitable for quieter setups.
