How To know what Ethernet cable I have
Did you know that 68% of home network issues stem from using the wrong Ethernet cable? Imagine buffering mid-game or losing a critical work call, all because of an unmarked Cat5e cable masquerading as a high-speed Cat6. In today’s connected world, your Ethernet cable isn’t just a cord; it’s the backbone of your digital life.
Using the wrong cable can slow down your internet speed, which will turn your 4K streaming experience into a pixelated mess. Gamers might blame their ISP for lag, not realizing their outdated Cat5 cable is the true problem. Here are the step by step methods to identify your cable, avoid compatibility nightmares, and choose the perfect upgrade. Keep reading to transform your network from sluggish to stellar!
Table of Contents
How to Identify Ethernet Cable Type by Looking at It
Color Coding and Jacket Materials
Ethernet cables often sport jackets in colors that hint at their type:
- Blue: Frequently used for Cat5e, a common choice for basic setups.
- Gray: Often signals Cat6, popular in modern installations.
- Yellow or Black: May indicate outdoor or direct burial cables designed for rugged conditions.
Color isn’t standardized, though, so don’t rely on it alone. The jacket material offers more dependable clues:
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Standard for indoor cables, balancing cost and durability. It’s flexible but not fire-resistant.
- PE (Polyethylene): UV- and water-resistant, perfect for outdoor runs exposed to the elements.
- LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen): Emits minimal smoke and no halogens when burned, a must for plenum spaces like ceilings or air ducts where fire safety is paramount.
Pro Tip: In commercial buildings, fire codes often require LSZH cables to protect occupants during emergencies.
Identify Ethernet Cable Ends
Most Ethernet cables use RJ45 connectors, but their design can reveal the cable’s category:
- Unshielded RJ45: Typical for Cat5e and Cat6, fine for low-interference areas like homes.
- Shielded RJ45: Found on Cat6a, Cat7, and Cat8, with metal casings to block EMI in noisy settings like factories.
- Gold-Plated Contacts: Suggest higher quality, minimizing signal loss and resisting corrosion over time.
Cable thickness and flexibility also provide hints. Cat5e and Cat6 are slim and pliable, easy to route through tight spaces. Cat7 and Cat8, with their extra shielding, are thicker and stiffer, reflecting their advanced capabilities.
Ethernet Cable with No Markings: What to Do
There exist ethernet cables without markings, due to wear, custom cuts, or cheap manufacturing, pose a challenge. You might find these in older homes, DIY setups, or bulk installations. While trickier, identification is still possible with a keen eye and some detective work.
Step-by-Step Visual Inspection
- Examine the Connector: Shielded (metal) connectors suggest Cat6a or higher; plastic ones lean toward Cat5e or Cat6.
- Feel the Jacket: Thicker, less flexible cables often indicate shielding, pointing to Cat7 or Cat8.
- Note the Color: Blue might hint at Cat5e, gray at Cat6, though this varies by manufacturer.
- Peek Inside (Safely): If you can strip a small section, tighter twists or shielding (foil or braiding) signal a higher category.
Alternative Identification Methods
- Review Purchase History: Dig up receipts or packaging from your original buy, they often list the category.
- Ask the Manufacturer: Some cables have batch codes or serial numbers traceable through customer support.
- Test It: When visuals fail, a cable tester (detailed later) offers a definitive answer.
Pro Tip: Label cables during installation with a marker or tag to avoid this headache later.
Decoding Ethernet Cable Types and Speeds
The jacket’s printed text, or “legend,” is your most reliable identifier. It typically includes:
- Category: Clear labels like “Cat6” or “Category 5e Enhanced.”
- Wire Gauge (AWG): E.g., “24 AWG” (thicker wires support better performance; 23 AWG is common in higher categories).
- Shielding: “UTP” for unshielded, “STP” or “SFTP” for shielded.
- Certifications: “UL,” “ETL,” or “TIA/EIA-568-B” confirm compliance with industry standards.
A Quick Task: HOW DO YOU DECODE THIS:
“Cat6a 23 AWG STP UL Listed”
A legend like “Cat6a 23 AWG STP UL Listed” is decode in common language is Category 6 Augment cable with 23 American Wire Gauge Shielded Twisted Pair Underwriters Laboratories Listed cable which means a high-quality, shielded cable built for 10 Gbps over long runs.
What Are Ethernet Cables?
Ethernet cables are like the highways for your internet. They carry data between devices like routers, switches, and computers. They’re organized into categories, abbreviated as “Cat” followed by a number or letter, each designed for specific speeds, bandwidths, and environments. Understanding these categories is your first step toward identifying and matching your cable to your network’s needs. Read in detail about the Ethernet cables.
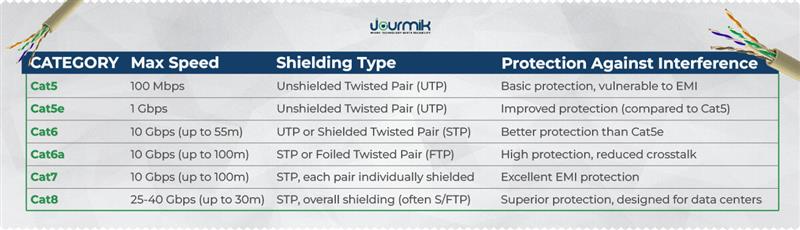
Common Ethernet Cables
Here’s a comprehensive rundown of the most common Ethernet cables kinds, their technical specs, and where they shine:
- Cat5: An aging standard, Cat5 supports speeds up to 100 Mbps with a 100 MHz bandwidth. It’s obsolete mainly but lingers in older setups like small offices or legacy phone systems.
- Cat5e (Enhanced): A refined version, Cat5e handles 1 Gbps at 100 MHz. It’s affordable and widely used for essential home networks, though it struggles with data-heavy tasks like 4K streaming.
- Cat6: Stepping up, Cat6 delivers 10 Gbps over 55 meters with 250 MHz bandwidth. Its improved crosstalk resistance makes it a favorite for modern homes and small businesses.
- Cat6a (Augmented): With 10 Gbps over 100 meters and 500 MHz bandwidth, Cat6a excels in larger setups. Enhanced shielding protects against interference, ideal for busy offices or homes with multiple devices.
- Cat7: Offering 10 Gbps at 600 MHz, Cat7 boasts advanced shielding (individual pair shields plus an overall shield). It’s built for industrial environments or data centers where electromagnetic interference (EMI) is a constant threat.
- Cat8: This cutting-edge technology achieves 40 Gbps over 30 meters with a massive 2,000 MHz bandwidth. It’s engineered for high-performance networks like server farms or enterprise backbones.
Technical Differences and Performance Impact
Each category’s performance hinges on factors like wire thickness, shielding, and twist rates:
- Shielding: Cat5e and Cat6 often use unshielded twisted pairs (UTP), while Cat6a, Cat7, and Cat8 add foil or braided shielding to combat interference.
- Crosstalk: Higher categories feature tighter twists and better insulation, reducing crosstalk (signal bleed between wires) for clearer data transmission.
- Cable Length: Distance affects speed. For instance, Cat6 supports 10 Gbps up to 55 meters but drops to 1 Gbps beyond that, while Cat6a maintains 10 Gbps up to 100 meters.
These distinctions matter whether you’re running a short cable to your gaming console or a long one across a warehouse. Matching the cable to your needs ensures optimal performance without overspending. Read more: Ethernet Cables
Ethernet Cable Speeds and Performance
Since now you are able to identify the ethernet cable you have it’s time to understand the types of the cables and the each category aligns with specific speeds and distances, here is the table that gives the overview for all cables;
| Cable Type | Max Speed | Max Distance | Best Use Case |
| Cat5e | 1 Gbps | 100 meters | Basic browsing |
| Cat6 | 10 Gbps | 55 meters | Streaming and gaming |
| Cat6a | 10 Gbps | 100 meters | Larger networks |
| Cat7 | 10 Gbps | 100 meters* | EMI-heavy areas (top shielding) |
| Cat8 | 40 Gbps | 30 meters | Data centers |
Conclusion
Mastering Ethernet cable identification unlocks a faster, more reliable network. Whether you’re decoding a Cat6’s legend, testing a mystery cable, or choosing Cat8 for a high-stakes project, you’re now equipped to succeed. Check your setup today are your cables holding you back?
Upgrade with Jourmik’s Ethernet cables and unleash your network’s full power!
FAQs
How do I identify my Ethernet cable?
Check the cable’s jacket for printed text (e.g., “Cat6”) or inspect the connector and shielding. Use a cable tester for unmarked cables.
How do I tell if I have Cat5 or Cat6?
Look for markings like “Cat5e” or “Cat6” on the cable jacket. Cat6 cables are typically thicker and have tighter wire twists compared to Cat5e.
How do I check my Ethernet type?
Examine the cable’s legend (printed text) for its category (e.g., Cat6, Cat7). If unmarked, use a cable tester or compare its thickness and shielding to known standards.
How do I know what type of Ethernet cable I need?
Match the cable to your network’s speed and distance requirements. For example, Cat6 is ideal for gaming, while Cat8 suits data centers.
How do I check my Ethernet specs?
Look for details like “Cat6a 23 AWG STP” on the cable jacket, which indicates category, wire gauge, and shielding type.
Is Cat6 good for gaming?
Yes, Cat6 supports speeds up to 10 Gbps and is excellent for gaming, offering low latency and high performance.
Is Cat6 Ethernet good?
Absolutely. Cat6 is versatile, supporting high speeds and bandwidth, making it suitable for streaming, gaming, and office networks.
How to trace an Ethernet cable?
Use a cable tracer tool or toner to follow the cable’s path. Labeling cables during installation can also simplify tracing later.
